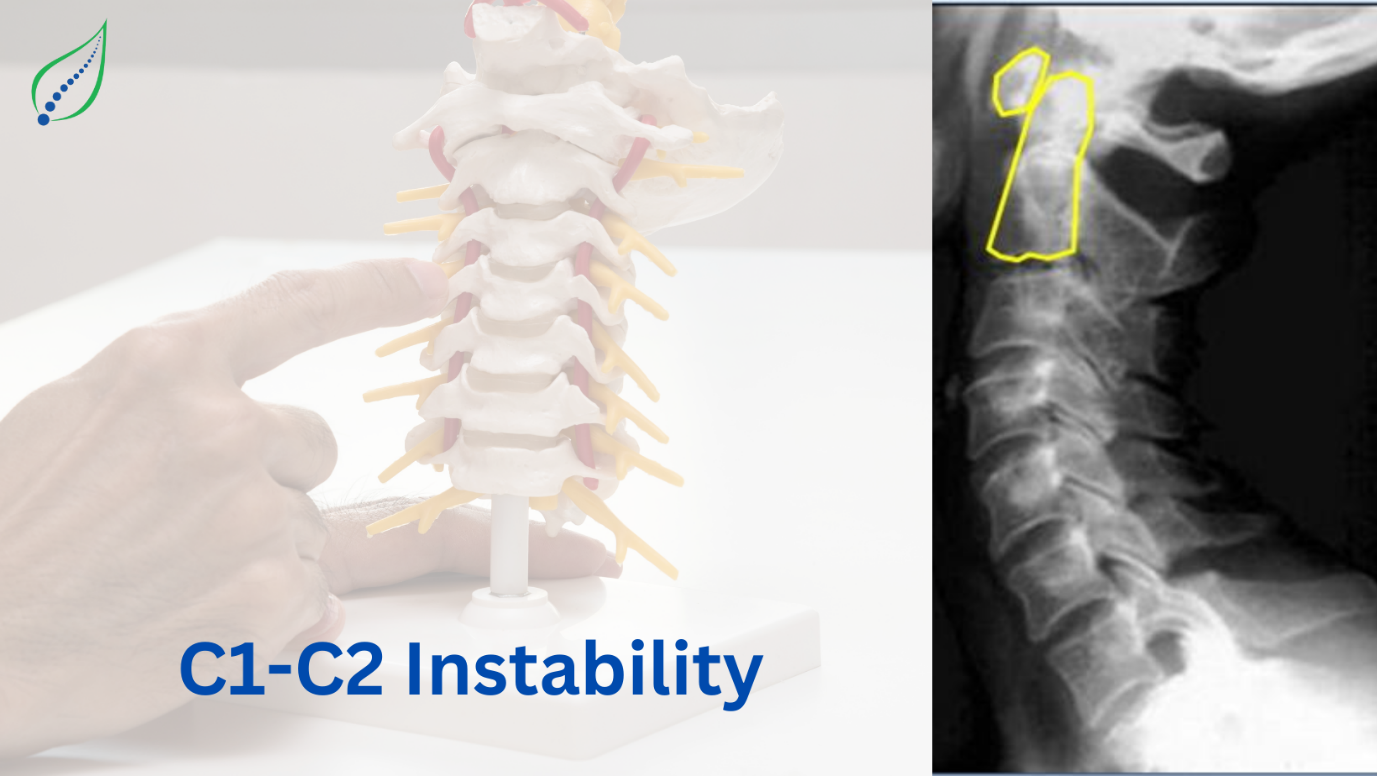
C1-C2 instability
Atlantoaxial instability also known as C1-C2 instability. It occurs due to excessive movement at the junction between the atlas and axis bone of the cervical spine as a result of ligamentous abnormality. It may also be congenital.
The atlantoaxial segment consists of the atlas C1 & axis C2 and forms a complex transitional structure bridging the occiput & cervical spine. The atlantoaxial joint is the most mobile joint with several neurovascular structures traversing through it. It has two functions:
- providing support for the occiput level
- providing the range of motion & flexibility while maintain stability.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY:
Atlantoaxial instability can be classified into three categories: inflammatory, congenital, and traumatic.
RA is common inflammatory disease affecting the craniovertebral level. It is due to a large number of synovial joints and ligaments contributing to the stability of the upper cervical spine.
The chronic inflammation of RA leads to laxity and stretching of the transverse ligament, development of granulation tissue & erosion of the bony structures to resulting in atlantoaxial subluxation & instability.
CAUSES :
In adult Degenerative changes :
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Atlas fractures
- Transverse ligament injuries
Paediatric causes:
- JRA
- Lysosomal storage disorder
- Trauma & infection
- Rotatory atlantoaxial subluxation
SYMPTOMS:
- Myelopathic symptoms
- Neck gets stuck or lock with movements
- Head feels heavy
- Broad based gait
- Decreased hand dexterity
- Loss of motor milestones
- Neck cannot support the weight of your head
- Head is tilted on top of your neck, inability to hold head up
- Intracranial hypertension- pressure headaches
- Arterial and Venous Compression related symptoms
- Brian fog, concentration difficulties, memory issues
INVESTIGATION :
- X-Ray
- MRI & CT scan
TREATMENT:
- Medication : Both over the counter and prescription medications help relieve vertebral injury and nerve pain.
- Immobilization: The use of a rigid neck collar & neck braces such as halo-thoracic brace are used in fractures and dislocations of the C1-C2 vertebrae.
- Manual therapy : It is an effective treatment for headaches, poor posture, and spinal alignment.
Physical therapy includes:
- Posture education
- Joint mobilization
- Soft tissue mobilization
- Spinal manipulation
- Proprioception exercises
- Chin tucks are the common strengthening exercise used in improve cervical instability.
- Isometric exercises with active range of motion to strengthen the neck area.
- Rotating the neck slowly and methodically strengthens the joints and muscles around the upper cervical spine.
_1746449195_1751827240.png)