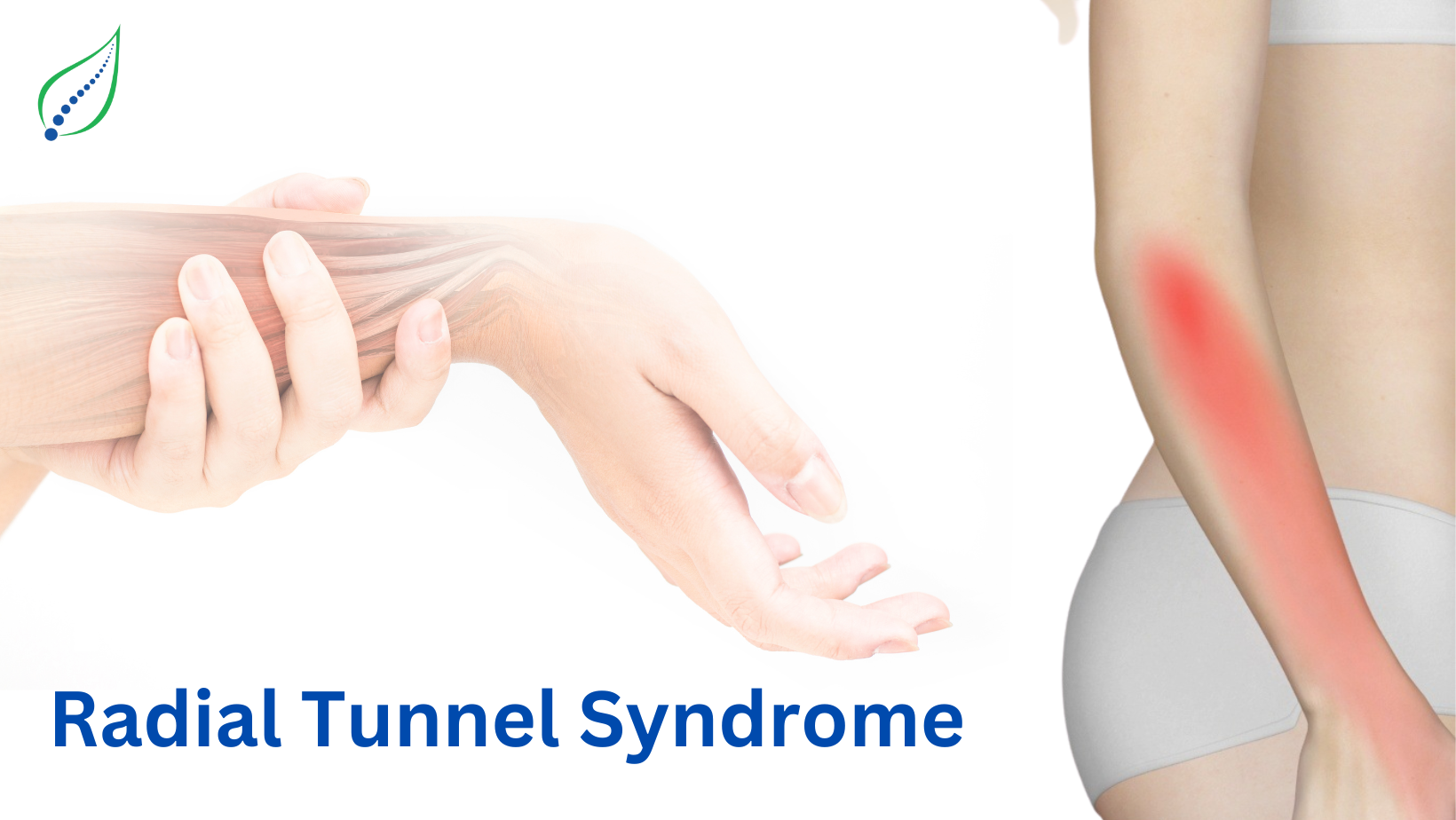
Radial Tunnel Syndrome
Entrapment of the posterior interosseous nerve in the proximal forearm maybe associated with pain & tenderness without motor loss leading to radial tunnel syndrome or with motor loss causing posterior interosseous nerve syndrome. Condition can often be associated with tennis elbow. Compression occurs at the radial tunnel, most common site being Arcade of Frohse.
The radial tunnel is a 5 cm potential space in the dorsal aspect of the forearm extending from the level of the radio-capitellar joint to the proximal edge of the supinator. Laterally it is bordered by the brachioradialis, ECRL, and ECRB muscles. The medial border consists of the biceps tendon and brachialis muscle. The floor of the radial tunnel is the capsule of the radio-capitellar joint.
Sites of compression:
- Fibrous band over radio-capitellar joint
- Synovitis of radio-capitellar joint
- Vascular leash of Henry
- Proximal fascial edge of ECRL muscle
- Arcade of Frohse
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY:
- It occurs by compression on the radial nerve from the radial head to the inferior border of the supinator muscle, without obvious extensor muscle weakness. Compression could happen in five different sites but the Arcade of Frohse is the most common area where the radial nerve is compressed.
- Bone fractures, trauma to the soft tissues surrounding the nerve, or repetitive elbow motion resulting in inflammation of the muscle can all result in radial tunnel syndrome.
SYMPTOMS :
- Presentation of pain- 3-5 cms distal to lateral epicondyle.
- Location of pain - Lateral elbow & dorsal forearm pain which may radiate to wrist & dorsum of fingers.
- Type of pain- Deep aching pain in the proximal forearm at the dorsal radial aspect. Diffuse vague pain more distal than lateral epicondylitis.
- Pain aggravates while forearm rotation, bending & lifting activities
DIAGNOSIS:
- Physical Examination -
Tenderness in the extensor muscle mass of the forearm at the arcade of Frohse (3 - 5cms distal to lateral epicondyle)
Pain during resisted supination and long finger extension, weakness of thumb, finger & extensor carpi ulnaris.
Additionally, wrist flexion and passive pronation can reproduce the dorsoradial proximal forearm pain by increasing the pressure in the radial tunnel to 250 mm Hg.
Doctor may suggest XRAY- Elbow & forearm or MRI for muscle oedema & atrophy along the course of posterior interosseous nerve
TREATMENT:
- Activity modifications
- Temporary splinting- With elbow in extension position & forearm in pronation & wrist flexion.
- Medications- No steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain. Your doctor may suggest local corticosteroid injection.
- Physical Therapy- Wrist & forearm stretches, strengthening the extensor muscle group (finger & wrist extensors, supinator) performing radial nerve glides.
_1750326150_1751826460.png)